El polvo del desierto juega un papel vital en la fertilización del crecimiento del fitoplancton en los océanos
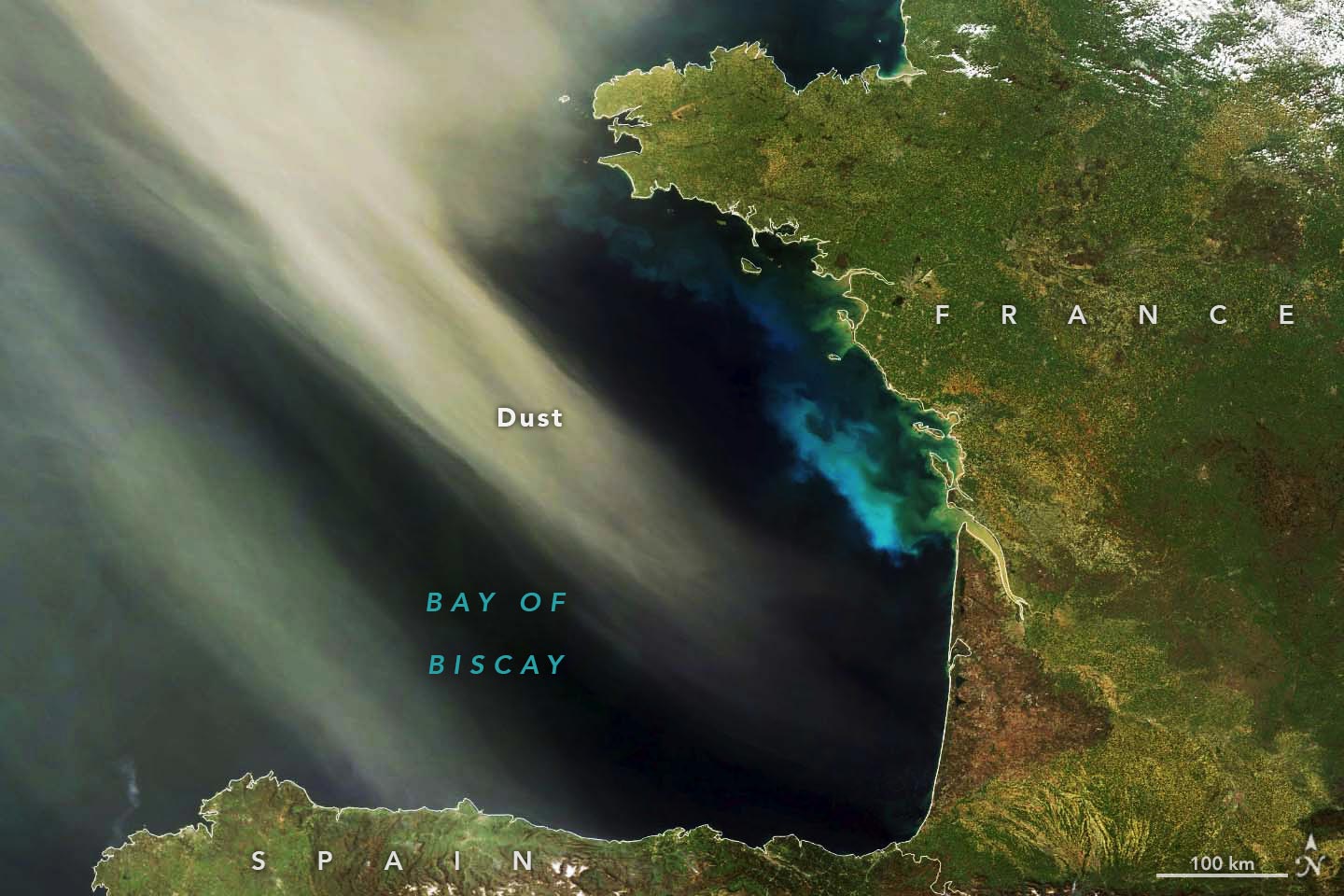


Esta imagen, adquirida el 8 de abril de 2011 con los instrumentos del espectrorradiómetro de imágenes de resolución moderada (MODIS) en el satélite Terra de la NASA, muestra el polvo del Sahara sobre el Golfo de Vizcaya. Una floración de fitoplancton hace que el agua se vea verde y azul brillante. Los sedimentos probablemente contribuyen con algo del color, especialmente en las áreas costeras. Crédito: Imagen del Observatorio de la Tierra de la NASA por Wanmei Liang, usando datos MODIS de la NASA EOSDIS LANCE y GIBS/Worldview
Un estudio publicado en Ciencia revela que el polvo mineral de la tierra juega un papel vital en la fertilización del crecimiento del fitoplancton en los océanos. Los investigadores combinaron observaciones satelitales y modelos informáticos para determinar que la deposición de polvo sustenta alrededor del 4,5 % de la producción de exportación mundial anual, con contribuciones que alcanzan el 20-40 % en algunas regiones. El fitoplancton, que es esencial para el clima de la Tierra, el ciclo del carbono y la red alimentaria marina, obtiene su energía de la luz solar y secuestra cantidades significativas de dióxido de carbono.
En las últimas décadas, los científicos han observado eventos naturales de fertilización del océano: episodios en los que columnas de ceniza volcánica, harina glacial, hollín de incendios forestales y polvo del desierto soplan sobre la superficie del mar y provocan una proliferación masiva de fitoplancton. Pero más allá de estos eventos extremos, hay una lluvia constante de partículas de polvo a larga distancia sobre el océano que promueve el crecimiento del fitoplancton durante casi todo el año y en casi todas las cuencas.
En un nuevo estudio publicado el 5 de mayo en la revista Cienciaun equipo de investigadores de la Oregon State University, la University of Maryland Baltimore County y[{» attribute=»»>NASA combined satellite observations with an advanced computer model to home in on how mineral dust from land fertilizes the growth of phytoplankton in the ocean. Phytoplankton are microscopic, plant-like organisms that form the center of the marine food web.
Phytoplankton float near the ocean surface primarily subsisting on sunlight and mineral nutrients that well up from the depths or float out to sea in coastal runoff. But mineral-rich desert dust — borne by strong winds and deposited in the ocean — also plays an important role in the health and abundance of phytoplankton.
According to the new study, dust deposition onto the ocean supports about 4.5% of yearly global export production — a measure of how much of the carbon phytoplankton take up during photosynthesis sinks into the deep ocean. However, this contribution approaches 20% to 40% in some ocean regions at middle and higher latitudes.
Phytoplankton play a large role in Earth’s climate and carbon cycle. Like land plants, they contain chlorophyll and derive energy from sunlight through photosynthesis. They produce oxygen and sequester a tremendous amount of carbon dioxide in the process, potentially on a scale comparable to rainforests. And they are at the bottom of an ocean-wide food pecking order that ranges from tiny zooplankton to fish to whales.
Dust particles can travel thousands of miles before falling into the ocean, where they nourish phytoplankton long distances from the dust source, said study coauthor Lorraine Remer, a research professor at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County. “We knew that atmospheric transport of desert dust is part of what makes the ocean ‘click,’ but we didn’t know how to find it,” she said.
Ocean Color Tells a Tale
How do you track ocean biology from 400 miles above the surface of Earth? Follow the green trail of chlorophyll.
Study authors Toby Westberry and Michael Behrenfeld — remote sensing oceanographers at Oregon State University — analyzed 14 years of ocean color measurements collected by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite from 2003 through 2016. Tracing distinct signatures in ocean color, they were able to determine not only when and where phytoplankton blooms occurred, but also how healthy and abundant they were (based on the concentration of chlorophyll).

This Sea-viewing Wide Field-of-view Sensor (SeaWiFS) image shows chlorophyll concentrations in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. Chlorophyll is the primary pigment found in phytoplankton—it gives the tiny marine plants their greenish color and they use it for photosynthesis. By precisely measuring the colors of light reflected by the ocean, SeaWiFS allows scientists to measure concentrations of phytoplankton blooms. In this false-color image, reds and yellows show high concentrations while greens, light blues, and dark blues show progressively lower concentrations. Black shows areas of no data due to cloud cover over the ocean. Credit: NASA SeaWiFS Project, Jim Gower, Institute of Ocean Sciences, Sidney BC, the IOS SERIES team, and Bill Crawford and Frank Whitney, Institute of Ocean Sciences, Sidney BC
To determine if the phytoplankton were responding to desert dust, the team compared their ocean color findings with output from NASA’s Goddard Earth Observing System (GEOS) model of dust deposition events for the same time period. These events ranged in intensity from mighty Saharan dust storms to relatively subdued plumes off the U.S. West Coast. They found that even modest amounts of desert dust increased the mass and improved the health of phytoplankton blooms almost everywhere they looked.
Previous studies had focused on large local events — volcanic eruptions, wildfires, extreme dust storms — that spewed huge amounts of organic and mineral particles into the air. In other studies, researchers intentionally stimulated phytoplankton growth by ‘seeding’ seawater with iron, a key but often limited nutrient in the ocean.
“We observed that the phytoplankton response wasn’t just happening in iron-poor areas of the ocean,” said coauthor Hongbin Yu, a scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. “The responses were occurring all over the world. Add a little bit of nutrients and you’ve got something happening in the water.”
The nutritional benefits of desert dust aren’t limited to iron, the scientists said. Dust particles contain other nutrients that plants need, notably phosphorus and nitrogen.
More research is needed as climate change impacts atmospheric patterns, soil moisture, and other factors that influence how dust journeys to the ocean, Remer said.
“For me,” she added, “the most interesting piece of what we accomplished here was bringing oceanographers and atmospheric scientists to the same table.”
Reference: “Atmospheric nourishment of global ocean ecosystems” by T. K. Westberry, M. J. Behrenfeld, Y. R. Shi, H. Yu, L. A. Remer and H. Bian, 4 May 2023, Science.
DOI: 10.1126/science.abq5252