An international team of scientists, led by E.E., has revealed seven countries that are immune foot soldiers
Neutral maps: They develop tools to fight cancer or most common immune cell infections
Spanish-led international team of scientists unveils seven states of immune infantry
The immune system keeps us alive, but it's still shrouded in mystery.An estimated $1.8 trillion distributed throughout the body is dedicated to protecting against infection or destroying cancer-causing cells.The most abundant of all and the first to react when problems arise are neutrophils, which quickly intervene to build bones like an army and travel through the blood.They do their job, catch microbes or ingest and die within a few hours.Although their existence has been known for more than a century, without knowing how they work, and it is not because they can help us, in infections such as covid, they are the cause of an excessive immune response that sometimes leads to death.
Alteration of the immune system has led to some of the most effective treatments against cancer and it is known that chronic inflammation, which occurs when the response to the threat does not go away, is behind many heart diseases or Alzheimer's.However, it is difficult to control for clinical use due to the complexity of the immune response and its sometimes ambiguous relationship to damage and healing.
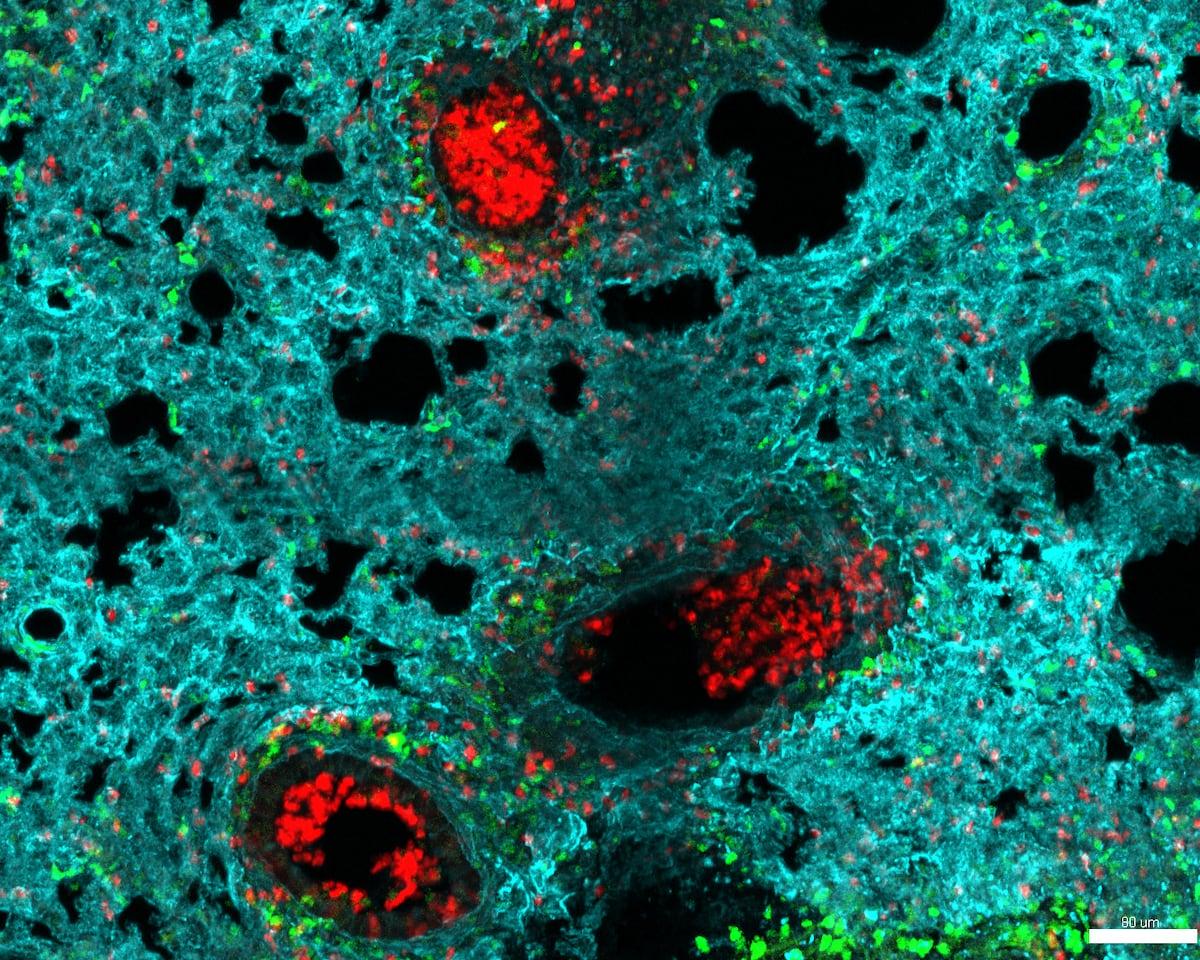
Today, an international team of scientists led by the National Cardiovascular Research Center (CNIC), Carlos III University of Madrid (UC3M), Yale University in the US and Westlake University publishes a map in the journal Nature that attempts to explain the complexity of neutrophils.After analyzing hundreds of thousands of neutrophils from mice, they changed our understanding of these cells and created NeuMap, the first map that describes the organization of neutrophils in different tissues, at different life stages and in different diseases.
"They are very simple cells, but they do very different things," says Iván Ballesteros, professor at UC3M and lead author of the study."When we started the project we didn't know what we would find, and we studied neutrophils in different situations, in pregnancy, in cancer, in lung disease... When we put them together and made this map, we saw that they are not so different and have only seven states."
According to Buysesos, although each netophile only lives for a few hours, together for a few hours, they maintain a stable arriring in their lives.They also see that there is a behavior conferred, which in some situations living with other people puts it in danger.
Within the seven stages of neutrophils, there are stages in which this army of immune cells is trained, others in which they silently circulate the blood waiting for the command to attack, and others in which they act against viruses or capture parts of pathogens to present to T lymphocytes for destruction.There are also some neutrophils that calm the immune response and prevent it from causing damage.However, in the second state, suppressing the immune response makes it easier for the cancer to thrive and form new blood vessels to feed it.
Knowing that neutrophils can adopt only seven states also facilitates the possibilities of acting on them.These cells do not always remain in the same state, but change depending on the circumstances, which opens up the possibility of manipulating these changes for medical purposes, such as blocking behavior that favors tumor growth.
"Because neutrophils are so plastic, and if you have an infection you have one type, and if you have a tumor we can very well know what type of cancer it is and what type of cancer it is and what type of infection it is, or if it's prone to sepsis, it can be helpful to identify it."
Second, they need to use their knowledge of Neutrophils to direct their activity to the right thing at any given time."You can't get rid of Neutrophils, because they are doing everything that is necessary, such as elimination in permission.
To achieve this goal, the researcher explains about the knowledge, he will use the knowledge he had with the students after studying in Neotrophil."They're like queens with queens, which brings children," he says.
In diseases such as cancer, when there is a response to Comiteterapy in a mouse model, it will acquire a specific pattern that activates the response against the cancer cells, Ballters said: "What we are trying to do is direct the futrophils to a state where they build vessels and destroy the tumor. "We believe that this system may be plastic," he added.
Neutrophils have been known for over a century, but technological advances such as extensive sequencing of single cells have begun to reveal their true identity.The new map of these cells is not only a resource for better understanding the immune system, but also a tool that could revolutionize medicine.
Your subscription is in use on another device
Do you want to add another user to your subscription?
If you continue to read on this device, it won't be able to read on another.
Your subscription arrow is used on another device and you can only access El PAís from one device at a time.
If you want to share your account, change your subscription to popular mode so you can add other users.Each person will log in with their own email account, allowing you to customize your El Paíals experience.
Do you have a business subscription?Sign up for more accounts here.
If you do not know who uses your account, we recommend changing your password here.
If you choose to continue sharing your account, this message will appear on your device and on the device of the other person using your account indefinitely, affecting your reading experience.You can view the terms and conditions of the digital subscription here.